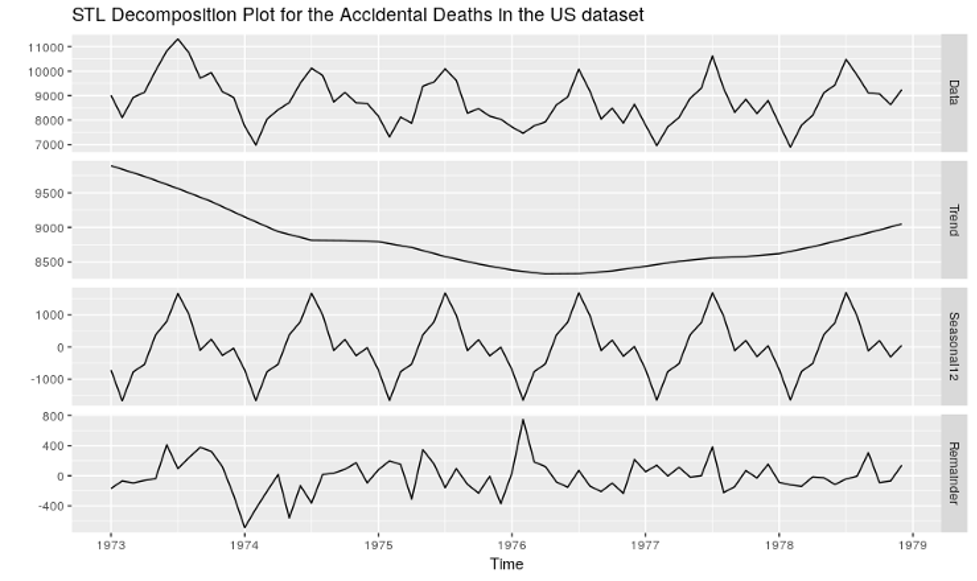
What Is “Blockchain”?
The most simplified definition is – It’s a shared ledger for recording the history of transactions – that cannot be altered.
A blockchain is a ledger of records arranged in data batches called blocks that use cryptographic validation to link themselves together. Put simply, each block references and identifies the previous block by a hashing function, forming an unbroken chain, hence the name.
Blockchain was invented by Satoshi Nakamoto in October 2008.
What’s a Block
Blockchain is a chain of blocks. A block is made of 2 parts Header and Body.
Header
The header consists of
- Previous block hash
- Current block hash
- TimeStamp
Body
Body contains all the assets/transaction details
The first block of any blockchain is called as Genesis Block, so at any node on the chain if you start tracking back you must reach the Genesis Block.
Blockchain = Data Store
In other words, the Blockchain can also be defined as a Special Data Store with following properties:
- Contains details of transactions
- Replicated across a number of systems – almost real-time
- Usually exists over a peer-to-peer network
- Uses cryptography and digital signatures to prove identity, authenticity and enforce read/write access rights
- Can be written by certain participants
- Can be read by certain participants, maybe a wider audience, and
- Has mechanisms to make it hard to change historical records, or at least make it easy to detect when someone is trying to do so.
Source:
Why Is Blockchain Hot Now?
Key Features of Blockchain:
- Shared Ledger: Append-only distributed system of records shared across the business network
- Smart Contract: Business terms are embedded in transaction database & executed with transactions
- Privacy: Ensuring appropriate visibility; transactions are secure, authenticated and verifiable
- Trust: Transactions are endorsed by relevant participants
Blockchain is Hot because,
- Having the distributed ledger, the processing time for decision can be brought down with the help of “Smart Contracts”.
- Data stored in the blockchain is a “Single Source of Truth” and being a “Permissioned Network”, the details will be accessible only by those who have the permission.
- Today, the Blockchain is solving a major problem of distrust.
- The Blockchain is a kind of a database with built-in validations. But this database/ledger is NOT stored in a single central location and NOT managed by any particular body. Rather it is distributed and existing on multiple computers at the same time.
Therefore, the reason for blockchain to trend across multiple industries is its attributes like being distributed and replicated over multiple systems & allowing for append-only data.
Popular Blockchain Platforms Compared
| Hyperledger Fabric + Hyperledger Composer |
Ethereum | |
| URL | Hyperledger Fabric, Hyperledger Composer | Ethereum |
| Open Source? | Yes | Yes |
| Open Source? | Yes | Yes |
| Governing Body | Hyperledger | Ethereum Foundation |
| UI Dashboard | No | No |
| Environment Setup Complexity | Medium | Medium + Continuous Running Process |
| Chaincode Framework | Native Fabric (GoLang) Hyperledger Composer (NodeJS) |
Solidity Truffle web3 |
| Learning Curve | Medium | High |
| Peers | Available | NA |
| Channels | Available | NA |
| Identity | Available | Accounts for each individual |
| Private Network | Available | Available (Continuously churning ethers) |
| Store Large Data | Yes | Yes (Complex) |
| Max Size of Data | No Limit | No Limit (0.02 microether per kb) |
| Store Image as a String | Yes | Yes |
| Store Video as a String | Yes | Yes |
| Encryption | Yes | Yes |
| Transaction Quality (Data Integrity) | 100% | 100% |
| Quality Of Smart Contract | Depends on the “Coding” | Depends on the “Coding” |
Blockchain Applications
In the context of blockchain, ‘Asset’ is a transactional or non-transactional entity. ‘Participants’ are the users who are dealing with the assets in the same network. Blockchain as a technology can have applications across various domains. Below are some prominent examples.
1. Asset Registration and Auctioning
- Asset:
- Vehicle
- Participants:
- Owner
- Auctioneer
- Buyer
- Insurer
- Government Regulator
- Use Case: A basic use case of the Asset Registration and Transfer of Ownership is, where multiple participants are on the common business network. Owner of the car can list his car along with the details on the network which can be seen by all other participants and buyer can bid for the car. The auctioneer has a choice to close this auction once a desired outcome is reached. Once the bidding is, ownership of the car will be automatically transferred to the buyer with the highest bid and at the same time buyer can get the required approvals from agencies like the insurer and the regulators.
- Benefits
- Accountability
- Transparency
- Faster process
- Cost-effective
2. Healthcare
- Asset:
- Medical Data
- Participants:
- Physician
- Patient
- Drug Chemist
- Use Case: In Healthcare, patient data is very critical and required at many levels, including the suggested drugs by the physician. Using blockchain, we can store patients’ medical records securely. Also, as blockchain is a “Permissioned” network, only relevant participants can access certain data within the medical records.
- Benefits
- High security
- Tamper-proof medical data
3. Supply Chain
- Asset:
- Any entity, e.g. Vegetables
- Participants:
- Manufacturer
- Supplier
- Retailer
- Government Regulators
- Use Case: In Supply Chain, asset lifecycle is the most critical piece of information. Blockchain can hold all the details of the asset at every stage of the supply chain.
This information like, when the container has been loaded by the manufacturer, what was the state of the asset at that time, etc. will be accessible by all participant on the network.
- Benefits
- Accountability
- Easy to track any losses/condition at each stage
- Recall “specific lot” rather than the entire stock
4. Audit and Compliance
- Asset:
- Financial Records
- Participants:
- Auditors
- Organization
- Financial Systems
- Regulators
- Use Case: In a large organization, financial data is scattered throughout many divisions and geographies. For the audit, we require indelible records of all the transactions over the reporting period. By using blockchain, we can collect the transaction records from a diverse set of financial systems. Append-only and tamper-proof qualities create high confidence financial audit trail and privacy feature to ensure only authorized user access.
- Benefits
- Cost-effective
- Speed up the process
- Accountability for each transaction
5. CryptoCurrency (BitCoin)
- Asset:
- BitCoin
- Participants:
- Anyone
- Use Case: BitCoin was the first application of the blockchain. BitCoin network allows the participants to transfer the bitcoins internally amongst the users. Users can only be identified by their address, which doesn’t have any relation to the real entity – the user.
- Benefits
- Anonymity
- Open Governance
Blockchain Use Cases
Following image contains the blockchain use cases across the industries.

Source:
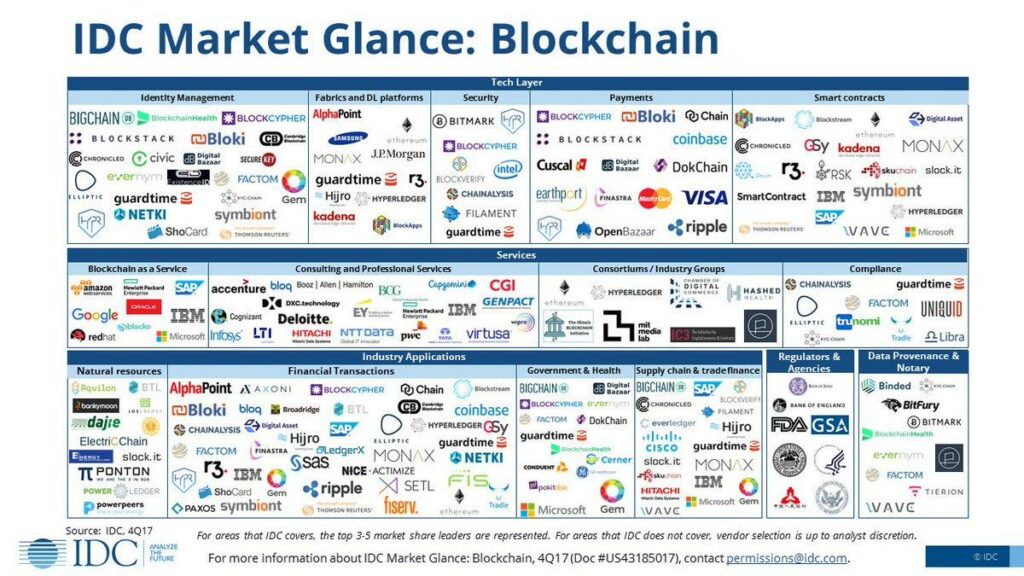
Blockchain Landscape
Following image contains the current blockchain landscape across industries.
Upcoming Trends
Farther-ranging blockchain applications have also seen venture backing, especially as the conversation has shifted from Bitcoin to blockchain at large. Companies like, Walmart, Unilever, Nestlé, and Dole has experimented “Food Safety” using blockchain. Identity Management and KYC is another area where blockchain is becoming very popular. Last but not the least, Supply Chain is the domain where blockchain is a perfect fit.